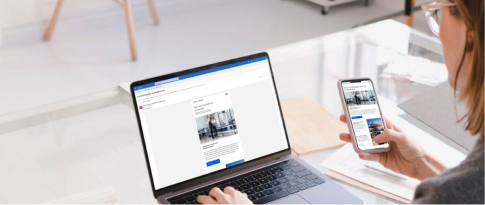
The EV market has grown significantly in the past few years. In 2023, nearly 3.2 million new electric car registrations were reported in Europe, showing an almost 20% increase relative to 2022. Countries like Germany, France, and the UK saw substantial growth in EV sales. Still, many buyers are confused by different electric drive configurations of EVs. This guide explains the primary types of electric vehicles and helps consumers make informed decisions.

4 Types of Electric Vehicles
There are multiple types of electric vehicles in the market. The main ones include:
1.BEV
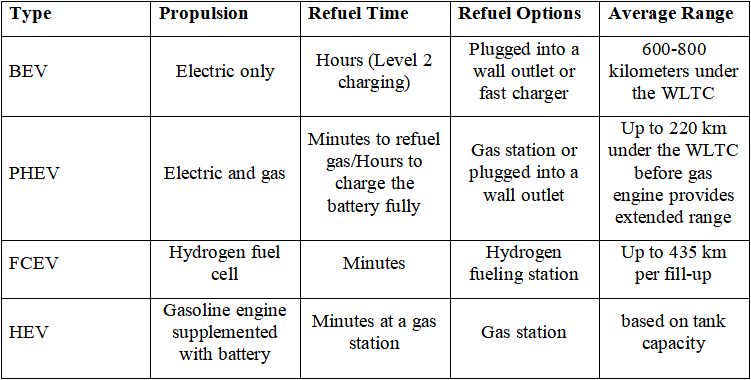
Battery Electric Vehicles operate solely on electricity stored in an onboard battery pack. Free from gasoline, they produce zero direct emissions. This electric vehicle type can be charged by plugging into standard electric outlets or fast chargers. The maximum range of BEVs can be 600-800 kilometers under the WLTC (Worldwide harmonized Light vehicles Test Cycles). This means BEVs efficiently meet daily needs without gas stops.
2.PHEV
Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles feature lithium-ion batteries and a gasoline engine. By plugging in when possible to charge batteries, the best electric vehicle models in this category can drive up to 220 km under the WLTC before the gas engine activates. This grants fuel efficiency and reduced emissions.
3.FCEV
Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles run on hydrogen fuel cells that chemically produce electricity. It can take only 10-20 minutes to top off the tanks of full cell electric trucks at hydrogen fueling stations. Though infrastructure lags behind other types of electric vehicles, FCEVs make compelling choices for commercial fleets due to their extended ranges of up to 435 km per fill-up.
4.HEV
Hybrid Electric Vehicles pair electric motors with efficient IC engines. As the power source of electric motors, HEV batteries can’t be charged by plugging in; instead, they derive electricity through IC engines and regenerative braking. This means HEVs deliver steady mileage gains without range or charge time concerns.
Comparison Table
The following comparison chart highlights the key distinctions between the four types of electric vehicles:

FAQs Regarding Electric Vehicles
With more drivers curious about electric vehicles, common questions frequently arise about their environmental impact, operation, and maintenance over time. These include:
Are Electric Vehicles Better for the Environment?
Electric vehicles produce little to no direct emissions during use. They result in smaller carbon footprints than gas cars over their life cycles. For instance, battery electric vehicles and fuel cell electric vehicles release no pollutants or greenhouse gases.
How Long Does it Take to Charge an Electric Vehicle?
Charging times vary based on the types of electric vehicles and the outlet used. It typically takes hours to fully charge a BEV and less than 1 hour with fast charging.
Do Electric Vehicles Have Transmissions?
While there is no multi-gear transmission like in gasoline cars, electric motors generate full torque instantaneously across their entire rpm range. This allows EVs to accelerate and brake efficiently using only direct drive. Some high-performance models might employ single-gear transmissions to reach higher top speeds.
How Long Will an EV Last?
With far fewer moving parts prone to internal wear and tear, electric vehicles are projected to require less maintenance and last over 100,000 miles. Batteries retain 70-80% capacity even after intensive use, and new cells can cost-effectively replace aging packs to restore a vehicle to like-new condition. Proper care further extends EV lifespans.
Conclusion
Electric vehicles are diversifying the transportation sector through innovative technologies. BEVs provide emissions-free mobility ideally suited for daily commuting. PHEVs extend electric driving distances economically. FCEVs are promising for heavy-duty and long-haul applications. And HEVs serve as an efficient transitional hybrid option.
Previous Repository
Subscribe
Receive the news that you are interested in.
Submit